The Bible (from Koine Greek τὰ βιβλία, tà biblía, “the books”) is a canonical collection of texts sacred in Judaism and Christianity. There is no single “Bible” and many Bibles with varying contents exist. The term Bible is shared between Judaism and Christianity, although the contents of each of their collections of canonical texts is not the same. Different religious groups include different books within their Biblical canons, in different orders, and sometimes divide or combine books, or incorporate additional material into canonical books. The Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, contains twenty-four books divided into three parts: the five books of the Torah (“teaching” or “law”), the Nevi’im (“prophets”), and the Ketuvim (“writings”). Christian Bibles range from the sixty-six books of the Protestant canon to the eighty-one books of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church canon. The first part of all Christian Bibles is the Old Testament, which contains, at minimum, the twenty-four books of the Hebrew Bible divided into thirty-nine books and ordered differently from the Hebrew Bible. The Catholic Church and Eastern Christian churches also hold certain deuterocanonical books and passages to be part of the Old Testament canon. The second part of the Christian Bible is the New Testament, containing twenty-seven books originally written in Koine Greek, which discuss the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christianity. The New Testament is divided into the four Canonical gospels, the Acts of the Apostles, twenty-one Epistles or didactic letters, and the Book of Revelation. By the 2nd century BCE Jewish groups had called the Bible books the “scriptures” and referred to them as “holy,” or in Hebrew כִּתְבֵי הַקֹּדֶשׁ (Kitvei hakkodesh), and Christians now commonly call the Old and New Testaments of the Christian Bible “The Holy Bible”, in Greek (, tà biblía tà ágia) or “the Holy Scriptures” (, e Agía Graphḗ). An early 4th-century Septuagint translation of the Hebrew Bible is found in the Codex Vaticanus. Dating from the 8th century, the Codex Amiatinus is the earliest surviving manuscript of the complete Vulgate Bible. The oldest Tanakh manuscript in Hebrew and Aramaic dates to the 10th century CE. The Bible was divided into chapters in the 13th century by Stephen Langton and into verses in the 16th century by French printer Robert Estienne and is now usually cited by book, chapter, and verse. The Bible is widely considered to be the best selling book of all time, has estimated annual sales of 100 million copies, and has been a major influence on literature and history, especially in the West where it was the first mass-printed book. The Gutenberg Bible was the first Bible ever printed using movable type.
- About
- Criminal Defense
- Consulting Services
- Prison Life
- Federal Prison Basics
-
-
-
OUR PRISON BOOKS
-
EARLY RELEASE FROM PRISON
-
-
- First Day in Federal Prison
-
-
-
OUR PRISON BOOKS
-
EARLY RELEASE FROM PRISON
-
-
- Information for Family Members
-
-
-
OUR PRISON BOOKS
-
EARLY RELEASE FROM PRISON
-
-
- Healthcare, Psychology, & Religion
-
-
-
OUR PRISON BOOKS
-
EARLY RELEASE FROM PRISON
-
-
- Prison Activities
-
-
-
OUR PRISON BOOKS
-
EARLY RELEASE FROM PRISON
-
-
- Trouble in Prison
-
-
-
OUR PRISON BOOKS
-
EARLY RELEASE FROM PRISON
-
-
- Help for Special Populations
-
-
-
OUR PRISON BOOKS
-
EARLY RELEASE FROM PRISON
-
-
- Federal Prison Basics
- Prison Life
-
-
-
-
-
Our Prison Books
Early Release from Prison
-
-
-
- Federal Prisons
- Federal Prisons
- News
- Booking
- Contact
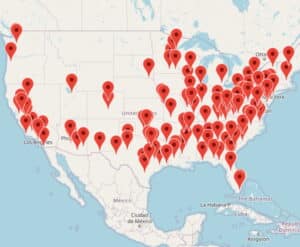
Federal Prison Information
We have profiled every prison within the Federal Bureau of Prisons.
Learn about each prison’s location, security level, educational and recreational offerings, and much more.
Other Office Locations
The information provided on this website is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. In some jurisdictions, this may be considered attorney advertising. Merely reading this information does not create an attorney-client relationship.
Our firm affiliates with local counsel licensed in their respective jurisdictions on a case-by-case basis. These local counsels are independent and are not employees of the firm. Please remember that when we reference our firm’s experience, this generally includes the combined expertise of both the firm and its frequently used local counsel.
The Law Office of Grant Smaldone is headquartered in Charleston, South Carolina. This is the only fully staffed office. References to any other city or state in any materials or anywhere on this website do not mean or otherwise indicate that the firm maintains an office in that location or has lawyers physically located in that city or state. The attorneys at the firm are licensed to practice law in only the jurisdictions listed in their biographies.
Every case is different, and any prior results mentioned on this website do not guarantee or suggest a similar result in other matters. There is no guarantee or assurance of success for any client.
The Law Office of Grant Smaldone limits its practice to South Carolina state and cases involving federal law and procedure.